Introduction:
In the realm of rechargeable battery technology, Nickel-Metal Hydride (NiMH) and 18650 Lithium-Ion (Li-ion) batteries stand as two prominent options, each offering unique advantages and drawbacks based on their chemical compositions and design. This article aims to provide a comprehensive comparison between these two battery types, examining their performance, durability, safety, environmental impact, and applications to assist users in making informed decisions.
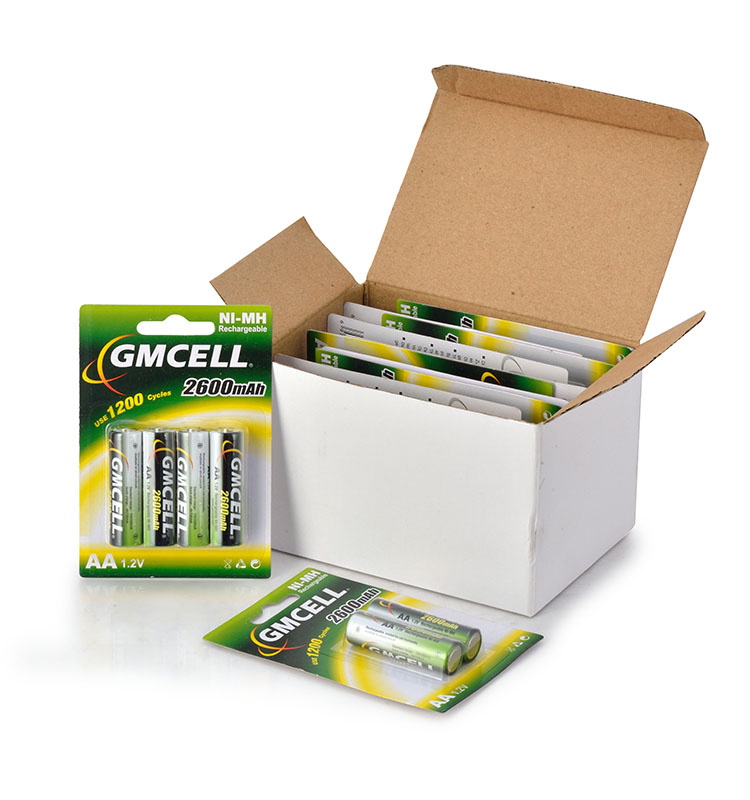

**Performance and Energy Density:**
**NiMH Batteries:**
**Pros:** Historically, NiMH batteries have offered a higher capacity than earlier forms of rechargeables, enabling them to power devices for extended periods. They demonstrate lower self-discharge rates compared to older NiCd batteries, making them suitable for applications where the battery might be unused for periods.
**Cons:** However, NiMH batteries have a lower energy density than Li-ion batteries, meaning they are bulkier and heavier for the same power output. They also experience a noticeable voltage drop during discharge, which can affect performance in high-drain devices.
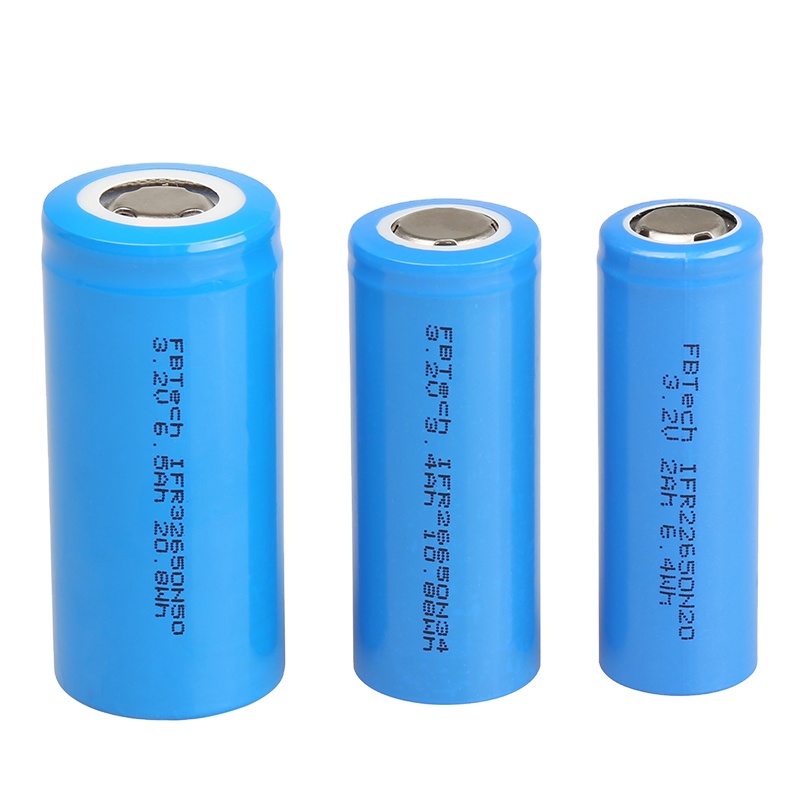

**18650 Li-ion Batteries:**
**Pros:** The 18650 Li-ion battery boasts a significantly higher energy density, translating to a smaller and lighter form factor for equivalent power. They maintain a more consistent voltage throughout their discharge cycle, ensuring optimal performance until nearly depleted.
**Cons:** Although they offer superior energy density, Li-ion batteries are more prone to rapid self-discharge when not in use, requiring more frequent charging to maintain readiness.
**Durability and Cycle Life:**
**NiMH Batteries:**
**Pros:** These batteries can withstand a greater number of charge-discharge cycles without significant degradation, sometimes reaching up to 500 cycles or more, depending on usage patterns.
**Cons:** NiMH batteries suffer from memory effect, where partial charging can lead to a reduction in maximum capacity if done repeatedly.

**18650 Li-ion Batteries:**
-**Pros:** Advanced Li-ion technologies have minimized the memory effect issue, allowing for flexible charging patterns without compromising capacity.
**Cons:** Despite advancements, Li-ion batteries generally have a finite number of cycles (approximately 300 to 500 cycles), after which their capacity decreases notably.
**Safety and Environmental Impact:**
**NiMH Batteries:**
**Pros:** NiMH batteries are considered safer due to their less volatile chemistry, presenting a lower fire and explosion risk compared to Li-ion.
**Cons:** They contain nickel and other heavy metals, requiring careful disposal and recycling to prevent environmental contamination.
**18650 Li-ion Batteries:**
**Pros:** Modern Li-ion batteries are equipped with sophisticated safety mechanisms to mitigate risks, such as thermal runaway protection.
**Cons:** The presence of flammable electrolytes in Li-ion batteries raises safety concerns, particularly in cases of physical damage or improper use.
**Applications:**
NiMH batteries find favor in applications where high capacity and safety are prioritized over weight and size, such as in solar-powered garden lights, cordless home appliances, and some hybrid cars. Meanwhile, 18650 Li-ion batteries dominate in high-performance devices like laptops, smartphones, electric vehicles, and professional-grade power tools due to their high energy density and stable voltage output.
Conclusion:
Ultimately, the choice between NiMH and 18650 Li-ion batteries depends on specific application requirements. NiMH batteries excel in safety, durability, and suitability for less demanding devices, while Li-ion batteries offer unmatched energy density, performance, and versatility for power-intensive applications. Considering factors such as performance needs, safety considerations, environmental impact, and disposal requirements is crucial in determining the most appropriate battery technology for any given use case.
Post time: May-28-2024