In modern life, batteries serve as an indispensable power source for various electronic devices. Alkaline and carbon-zinc batteries are the two most common types of disposable batteries, yet they differ significantly in performance, cost, environmental impact, and other aspects, often leaving consumers confused when making a choice. This article provides a comprehensive comparative analysis of these two battery types to help readers make informed decisions.
I. Basic Introduction to Alkaline and Carbon-Zinc Batteries
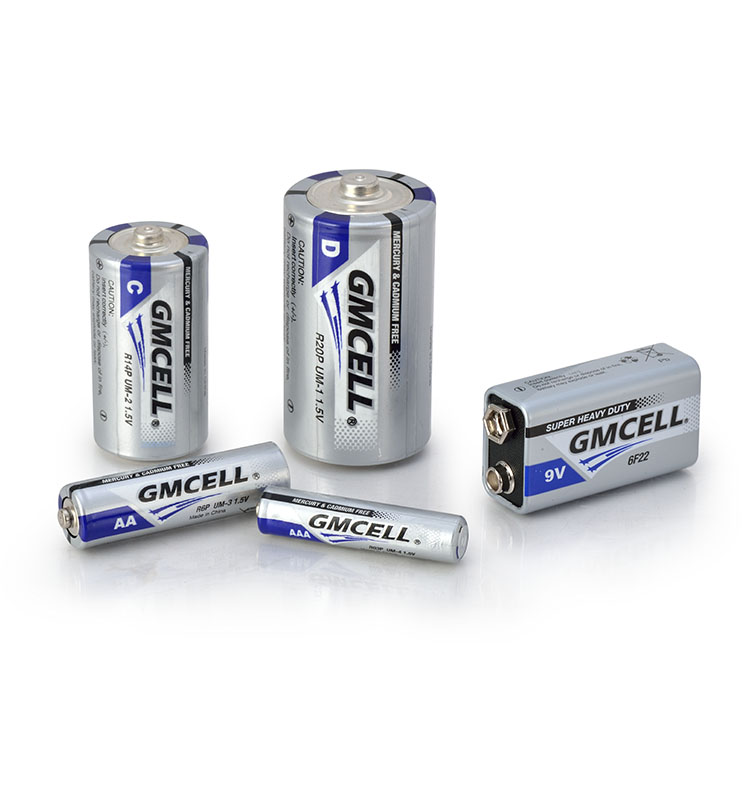
1. Alkaline Batteries
Alkaline batteries use alkaline substances such as potassium hydroxide (KOH) solution as the electrolyte. They adopt a zinc-manganese structure, with manganese dioxide as the cathode and zinc as the anode. Though their chemical reactions are relatively complex, they generate a stable voltage of 1.5V, identical to carbon-zinc batteries. Alkaline batteries feature optimized internal structures that enable long-term stable power output. For example, GMCELL alkaline batteries utilize advanced structural designs to ensure durable and consistent performance.
2. Carbon-Zinc Batteries
Carbon-zinc batteries, also known as zinc-carbon dry cells, use ammonium chloride and zinc chloride solutions as electrolytes. Their cathode is manganese dioxide, while the anode is a zinc can. As the most traditional type of dry cell, they have simple structures and low production costs. Many brands, including GMCELL, have offered carbon-zinc batteries to meet basic consumer needs.
II. Advantages and Disadvantages of Alkaline Batteries
1. Advantages
- High Capacity: Alkaline batteries typically have 3–8 times higher capacity than carbon-zinc batteries. For instance, a standard AA alkaline battery can deliver 2,500–3,000 mAh, while a carbon-zinc AA battery provides only 300–800 mAh. GMCELL alkaline batteries excel in capacity, reducing replacement frequency in high-drain devices.
- Long Shelf Life: With stable chemical properties, alkaline batteries can last 5–10 years under proper storage. Their slow self-discharge rate ensures readiness even after prolonged inactivity. GMCELL alkaline batteries extend shelf life through optimized formulations.
- Wide Temperature Tolerance: Alkaline batteries operate reliably between -20°C and 50°C, making them suitable for both freezing outdoor winters and hot indoor environments. GMCELL alkaline batteries undergo specialized processing for stable performance across conditions.
- High Discharge Current: Alkaline batteries support high-current-demand devices like digital cameras and electric toys, delivering rapid power bursts without performance drops. GMCELL alkaline batteries excel in high-drain scenarios.
2. Disadvantages
- Higher Cost: Production costs make alkaline batteries 2–3 times pricier than carbon-zinc equivalents. This may deter cost-sensitive users or high-volume applications. GMCELL alkaline batteries, while high-performing, reflect this price premium.
- Environmental Concerns: Though mercury-free, alkaline batteries contain heavy metals like zinc and manganese. Improper disposal risks soil and water pollution. However, recycling systems are improving. GMCELL is exploring eco-friendly production and recycling methods.
III. Advantages and Disadvantages of Carbon-Zinc Batteries
1. Advantages
- Low Cost: Simple manufacturing and cheap materials make carbon-zinc batteries economical for low-power devices like remote controls and clocks. GMCELL carbon-zinc batteries are competitively priced for budget-conscious users.
- Suitability for Low-Power Devices: Their low discharge current suits devices requiring minimal power over long periods, such as wall clocks. GMCELL carbon-zinc batteries perform reliably in such applications.
- Reduced Environmental Impact: Electrolytes like ammonium chloride are less harmful than alkaline electrolytes. GMCELL carbon-zinc batteries prioritize eco-friendly designs for small-scale use.
2. Disadvantages
- Low Capacity: Carbon-zinc batteries require frequent replacement in high-drain devices. GMCELL carbon-zinc batteries lag behind alkaline counterparts in capacity.
- Short Shelf Life: With a 1–2 year shelf life, carbon-zinc batteries lose charge faster and may leak if stored long-term. GMCELL carbon-zinc batteries face similar limitations.
- Temperature Sensitivity: Performance plummets in extreme heat or cold. GMCELL carbon-zinc batteries struggle in harsh environments.
IV. Application Scenarios
1. Alkaline Batteries
- High-Drain Devices: Digital cameras, electric toys, and LED flashlights benefit from their high capacity and discharge current. GMCELL alkaline batteries power these devices effectively.
- Emergency Equipment: Flashlights and radios rely on alkaline batteries for reliable, long-lasting power in crises.
- Continuous-Use Devices: Smoke detectors and smart locks benefit from alkaline batteries’ stable voltage and low maintenance.
2. Carbon-Zinc Batteries
- Low-Power Devices: Remote controls, clocks, and scales operate efficiently with carbon-zinc batteries. GMCELL carbon-zinc batteries offer cost-effective solutions.
- Simple Toys: Basic toys without high power needs (e.g., sound-making toys) suit carbon-zinc batteries’ affordability.
V. Market Trends
1. Alkaline Battery Market
Demand grows steadily due to rising living standards and electronics adoption. Innovations like rechargeable alkaline batteries (e.g., GMCELL’s offerings) blend high capacity with eco-friendliness, appealing to consumers.
2. Carbon-Zinc Battery Market
While alkaline and rechargeable batteries erode their share, carbon-zinc batteries retain niches in cost-sensitive markets. Manufacturers like GMCELL aim to enhance performance and sustainability.
Post time: Apr-10-2025